

boundary of the upper extremity and shaft of the ulna,While the bones of the carpus are somewhat confused on account of some overlapping, the metacarpals and phalanges are so clear that the spongiosa of the articular ends and the compacta of the shaft, together with the marrow cavity it encloses, may be made out the sesamoid bones are also distinct. lateral condyle of the humerus (the official nomenclature does not include condyles for the humerus, only epicondyles), The structure of the spongiosa is only indistinctly indicated. Human Anatomy Atlas.One sees the lower end of the humerus, about the upper third of the radius and ulna and the joint cavity, especially that of the humero-radial articulation.
Only the talus and calcaneus show extensive ossification that of the cuboid is already distinct the cuneiforms, except for a small center in the third, and the navicular are still entirely cartilaginous and consequently not visible in the photograph. Ossification is less advanced in the tarsal bones, which are for the great part still cartilaginous. In contrast, ossification is entirely wanting in both the cartilaginous epiphyses of the fibula.
The centers for the distal epiphyses of the four lateral metatarsals are in some cases double and it is noticeable that no epiphysial centers are to be seen at the proximal ends of the basal phalanges they are quite evident at the bases of the middle phalanges and the terminal phalanx of the great toe. All the tarsal bones show centers and epiphysial centers are visible in the metatarsals and some of the phalanges. boundary of the musculature and fatty tissue,Compared with the preceding figure a marked progress in the ossification of the foot bones is evident. center for the distal tibial epiphysis (faint), center for the proximal tibial epiphysis, center for the distal femoral epiphysis,
The liver is completely removed and the parietal peritoneum, together with the ascending and descending mesocolon, is dissected away from the kidneys, the most of the duodenum, the great vessels and the musculature, but retained in the true pelvis, being split, however, for a short distance over the ureters. The stomach is removed, except for the cardia and pylorus, and thereby the posterior wall of the bursa omentalis is exposed. double center for the distal epiphysis of metatarsal V.The anterior abdominal wall and the anterior part of the Diaphragm are cut away by a frontal section, except for a lower left flap. proximal epiphysial center of metatarsal I, Röntgen photographs of the foot are consequently less satisfactory than those of the flatter hand.
The arteries are injected with red wax mass. The urinary bladder is rather strongly distended. On the right the ductus deferens is exposed by opening up the inguinal canal down to the scrotum.
Human Anatomy Atlas 3D Skin And Facial
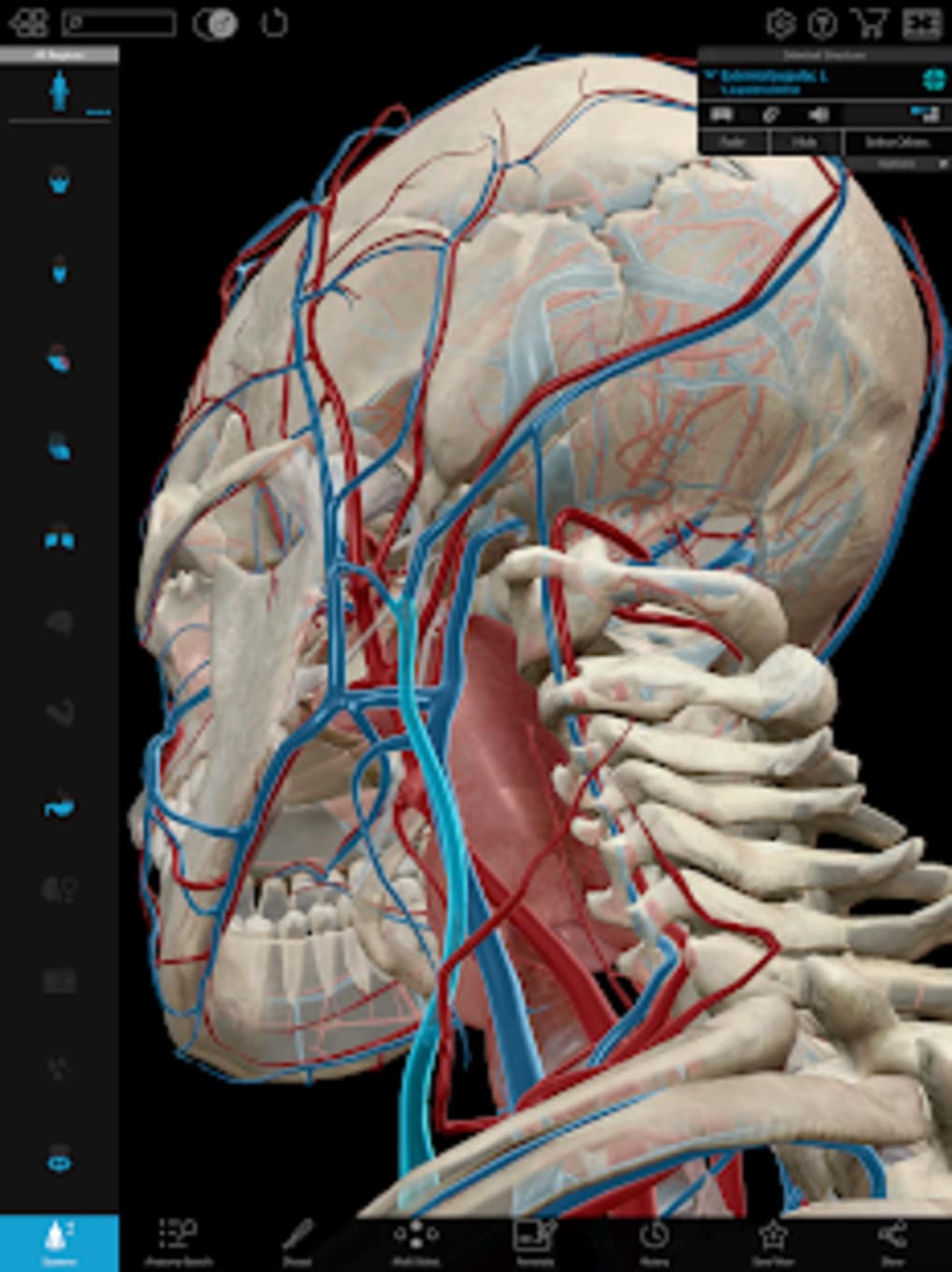
In the neck, by the removal of the Sternomastoideus and the internal jugular vein, the glossopharyngeal, vagus and hypoglossal nerves are shown.+ = anastomotic branch to glossopharyngeal nerve.+* = part of submaxillary gland above the Mylohyoideus.On the left is shown the arrangement of the paths traversing the internal capsule, in the anterior limb: the anterior thalamic radiation yellow, the frontal cerebro-pontile tract blue, the cortico-bulbar tract red striated (the genu of the capsule). In the orbit, in addition to the nerves to the orbital muscle, branches of trigeminus I are shown and some branches of trigeminus II of trigeminus III only the lingual nerve is fully retained. Only the anterior part of the mandible is retained the zygomatic bone and arch, with the muscles of mastication, are removed and also parts of the maxilla. The skin and facial musculature is completely removed and the orbit opened from the lateral side the base of the skull is cut away up to the foramen rotundum and the temporal bone cut along the facial canal.
As regards the methods of reproduction of the figures, polychromatic lithography is used for the first time - so far as I am aware - in anatomical illustrations. In the Myology the explanatory text takes the form of tables which give at a glance the origin, insertion, nerve supply and action of the muscles. This enables the student using the book during his dissection to review rapidly the chief points in his preparation. Any difficulty that might arise for the beginner by an unusual method of presentation of the figures has, therefore, been carefully avoided.The illustrations are so arranged that there is to be found on the opposite page, in addition to the explanation of the figures, a brief descriptive text. Consequently in the make-up of the book a limitation to what was absolutely necessary seemed to me a prime consideration.In its outward form this first volume of the work is treated throughout as an Atlas, is arranged primarily for use by classes in dissection and follows closely the usual methods employed in such classes.
For the names of parts the Basel Nomenclature has been used. Have been reproduced by line etching.For greater convenience special colors have been extensively used in the illustrations reproduced by the autotype process, a chamois tint for the bones in illustrations of the articulations and many of the muscle figures, different colors for the individual skull bones in representations of the entire skull and in topographic figures of the skull bones. In addition key-figures, diagrams, etc. For the other illustrations the so-called autotype process is used, and its suitability for the purpose may be seen from the Atlas itself. Nearly all the figures in the Myology are reproduced in this manner.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
